Eczema (Dermatitis)
What is Eczema?
Affecting between nine and thirty percent of the U.S. population, eczema refers to inflammation of the skin. The term eczema actually covers many various skin conditions that produce itchy, dry skin patches. Although it can appear anywhere on the body, eczema usually appears on the creases on the face, arms and legs. Because of the intense itching that accompanies eczema, people often scratch the skin which leads to crusting and oozing.
A non-contagious skin condition, eczema has no known cause. It does appear to have a hereditary component. Certain things, such as stress, weather and environmental factors can trigger a flare-up of eczema. People with eczema often live with cycles of flare-ups and remissions.
In mild cases of eczema, over-the-counter topical creams and antihistamines can relieve the symptoms. More severe eczema may require stronger medications, such as steroid creams, oral steroids (corticosteroids), and antibiotic pills or antifungal creams to treat any potential infection. Using mild cleansers and keeping skin moist can help control your eczema.
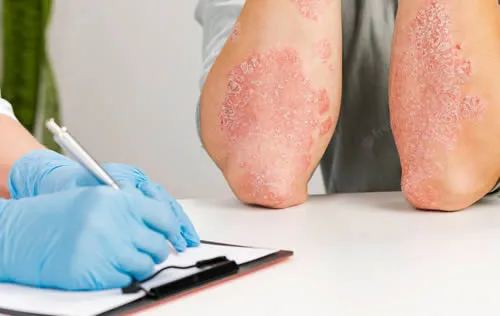
What are the signs and symptoms of Eczema?
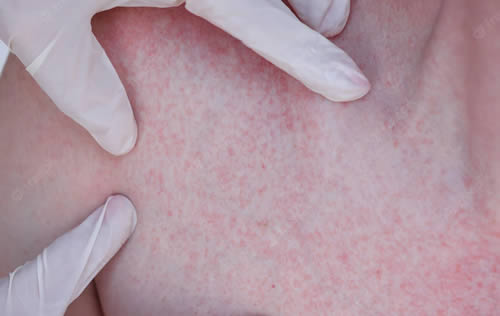
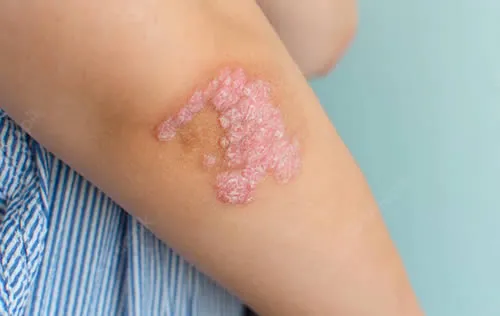
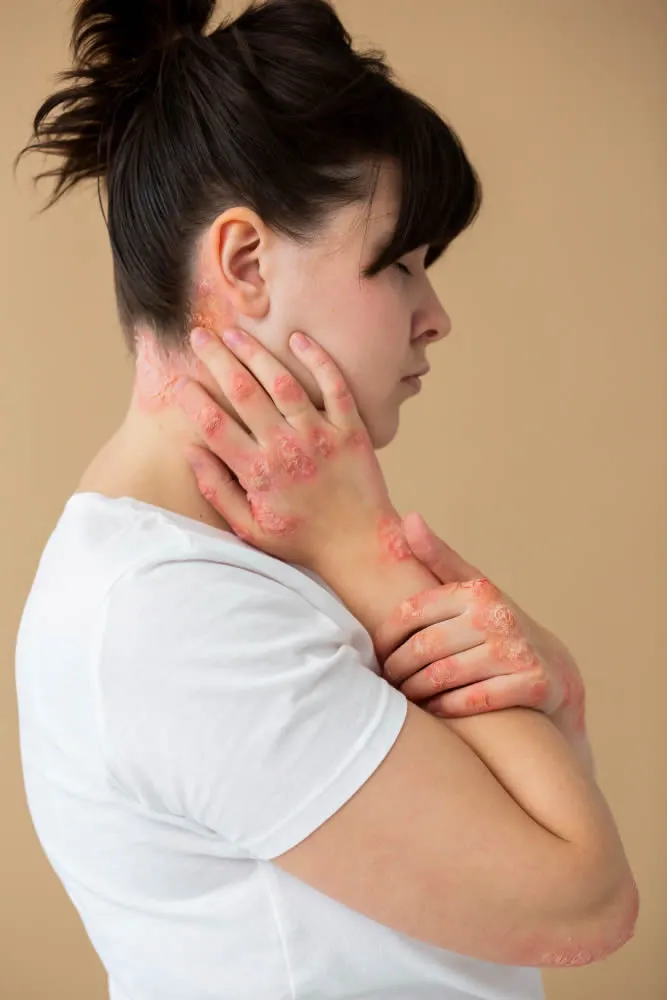
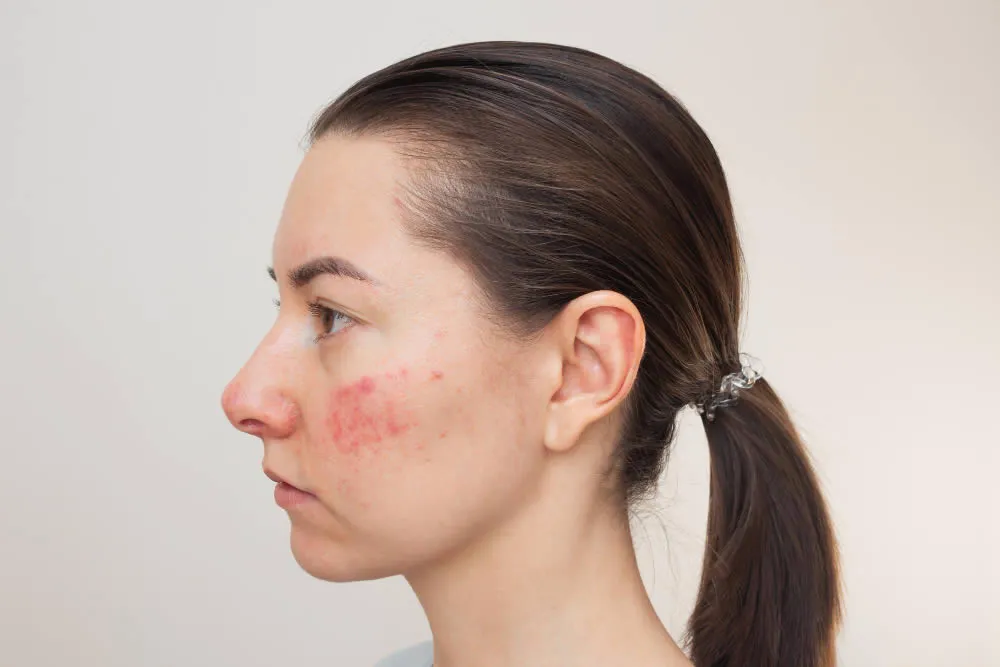
Eczema is a condition that causes your skin to become dry, itchy and inflamed. The signs and symptoms of eczema can vary depending on the type, severity and stage of the condition. Some common signs and symptoms of eczema are:
- Dry, cracked, scaly or flaky skin
- Red, pink, purple, brown or gray patches of skin
- Itching, which may be worse at night or during flare-ups
- Small, raised bumps that may ooze or crust over
- Thickened, leathery or discolored skin from scratching
- Swelling or inflammation of the skin
- Rash on the face, neck, hands, elbows, knees, ankles, feet or other areas of the body
What are the causes of Eczema?
Eczema is a condition that causes your skin to become dry, itchy and inflamed. The causes of eczema are not fully understood, but they may include:
- A genetic variation that affects the skin’s ability to provide protection from bacteria, irritants, allergens and environmental factors.
- An imbalance of the bacteria on the skin, which disrupts the skin’s barrier function and triggers an immune system response.
- A contact with a trigger in your environment, such as dry weather, fabrics, makeup, smoke, soaps or detergents.
- A history or diagnosis of dermatitis, allergies, hay fever or asthma.
- A physical or emotional stress, which can cause inflammation in the body.
What treatments are available at the dermatologist for Eczema?
There are different treatments available at the dermatologist for eczema, depending on the type, severity and cause of the condition.
Some of the possible treatments are:
- Medicated creams or ointments that control itching, inflammation and infection. These may include corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, antibiotics or antifungals.
- Oral medications that suppress the immune system or reduce inflammation. These may include cyclosporine, methotrexate, prednisone, azathioprine or biologics.
- Phototherapy or light therapy, which uses ultraviolet (UV) rays to improve the skin’s condition and reduce symptoms.
- Patch testing or allergy testing, which helps identify specific substances that trigger or worsen eczema.
- Wet wraps or paste bandages, which cover the skin with moist dressings to soothe and protect it.
- Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers, moisturizing regularly, using gentle skin care products and managing stress.
The best treatment for eczema depends on your individual situation and preferences. Your dermatologist can help you find the most suitable and effective treatment for your eczema.

How to Avoid Common Eczema Triggers and Irritants
- Use a thick moisturizer (emollient) as a soap substitute when washing your body or hands. Avoid soap, bubble bath and shower gel completely, as they can remove the natural oils from your skin and make it dry and itchy.
- Wear cotton clothes next to your skin rather than potentially irritating fabrics such as wool. Wash your clothes with non-biological detergents and rinse them well. Avoid fabric conditioners, as they can also cause eczema to flare up.
- Keep your skin moisturized regularly, especially after bathing or showering. Apply a non-fragranced, dye-free cream or ointment to lock in the moisture and protect your skin barrier.
- Avoid contact with irritating chemicals and substances, such as fragrances, dyes, perfumes, alcohols, soaps and detergents. Wear rubber gloves with a cotton lining when using these products or working with similar chemicals.
The Benefits of Phototherapy for Eczema
Phototherapy is a treatment option that uses ultraviolet (UV) light to improve the symptoms of eczema, such as redness, itching, inflammation and infection. Some of the benefits of phototherapy for eczema are:
- It may help clear your skin by reducing the inflammation and destroying the bacteria that cause eczema.
- You may experience fewer eczema rashes in the future by strengthening your skin barrier and preventing the entry of external triggers.
- It may decrease the need for using topical medications, which can have side effects or lose effectiveness over time.
- It may also improve your mood and quality of life by relieving the discomfort and stress caused by eczema.
FAQ About Eczema
Are there different types of eczema?
What are the symptoms of eczema?
How is eczema diagnosed?
Can eczema affect other parts of the body besides the skin?
Can certain foods trigger eczema?
Is there a dermatologist near me in Spokane that offers treatment for exzema?
Yes. At our Spokane dermatology office we offer treatment for eczema to patients from Spokane and the surrounding area. Contact our office today to schedule an appointment.